
You can lower your risk of Cervical Cancer by getting screened regularly, starting at age 21.
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix… the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina.
Various strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection, play a role in causing most cervical cancer.
When exposed to HPV, the body’s immune system typically prevents the virus from doing harm. In a small percentage of people, however, the virus survives for years, contributing to the process that causes some cervical cells to become cancer cells.
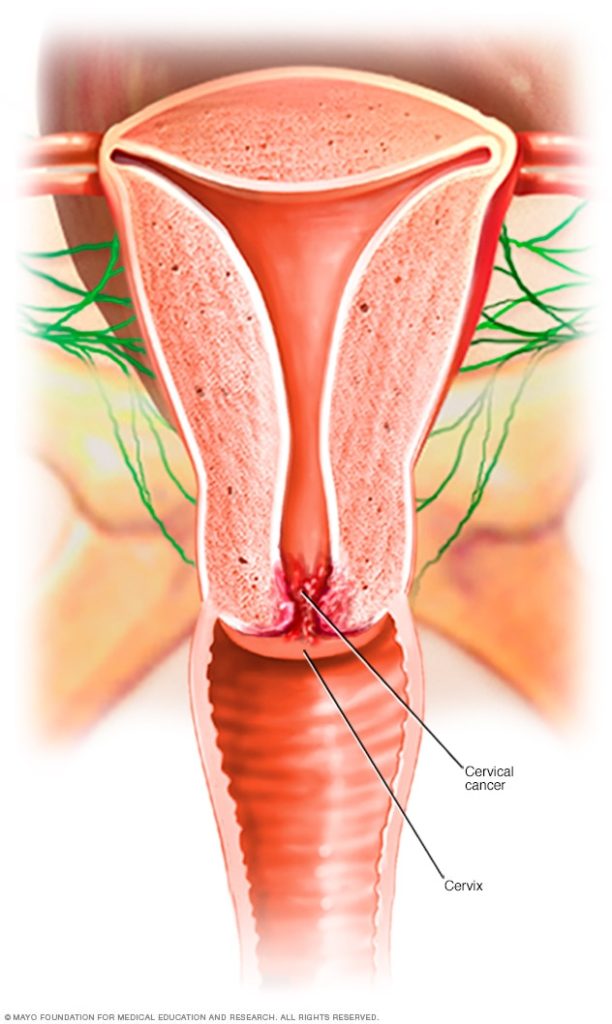
You can reduce your risk of developing cervical cancer by having screening tests and receiving a vaccine that protects against HPV infection.
Screening Tests
Two tests help prevent cervical cancer or find it early:
- The Pap test (or Pap smear) looks for precancers, which are cell changes on the cervix that might become cervical cancer if they are not treated appropriately.
- The human papillomavirus (HPV) test looks for the virus that can cause these cell changes.
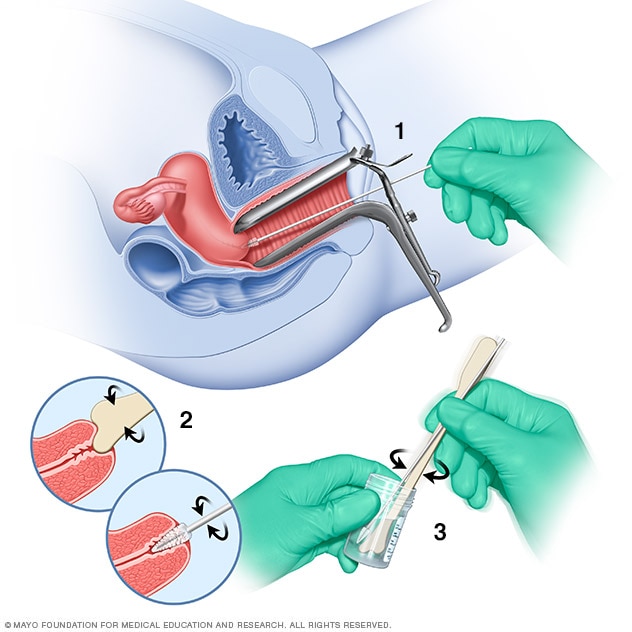
Screening Options
You should get your first Pap test at age 21. If your test result is normal, you can wait three years for your next test.
If you’re 30 years old or older, you have three options:
- You can continue getting a Pap test only. If your test result is normal, you can wait three years for your next test.
- You can get an HPV test only. If your test result is normal, you can wait five years for your next test.
- You can get both an HPV and Pap test together. If your test results are normal, you can wait five years for your next tests.
HPV Vaccine
The HPV vaccine protects against the types of HPV that most often cause cervical cancers. HPV can also cause other kinds of cancer in both men and women.
- HPV vaccination is recommended for preteens aged 11 to 12 years, but can be given starting at age 9.
- HPV vaccine also is recommended for everyone through age 26 years, if they are not vaccinated already.
- HPV vaccination is not recommended for everyone older than age 26 years. However, some adults age 27 through 45 years who are not already vaccinated may decide to get the HPV vaccine after speaking with their doctor about their risk for new HPV infections and the possible benefits of vaccination. HPV vaccination in this age range provides less benefit, as more people have already been exposed to HPV.
HPV vaccination prevents new HPV infections, but does not treat existing infections or diseases. This is why the HPV vaccine works best when given before any exposure to HPV.
You should get screened for cervical cancer regularly, even if you received an HPV vaccine.
